Between 2018 and 2024, nearly 70 million academic and professional documents were analyzed by PlagiarismSearch.com, offering one of the most comprehensive views into the evolving dynamics of plagiarism worldwide. The seven-year dataset captures dramatic shifts in writing behaviors influenced by global disruptions and technological advances.
The study identifies three primary drivers shaping global plagiarism trends: the transition to remote education during the COVID-19 pandemic, the widespread adoption of AI-powered writing tools such as ChatGPT, and evolving national policies on academic integrity. Each of these factors impacted the way students, institutions, and educators approached written assessments, often in unpredictable ways.
According to the data, the global average plagiarism rate more than doubled between 2018 and 2020, rising from 9.08% to 18.79%. This spike closely coincided with the abrupt global pivot to online learning, where many institutions struggled to enforce academic standards amid reduced instructor oversight and insufficient digital monitoring systems. The trajectory of these shifts is illustrated in the chart below, highlighting both pandemic-related and AI-related disruptions.
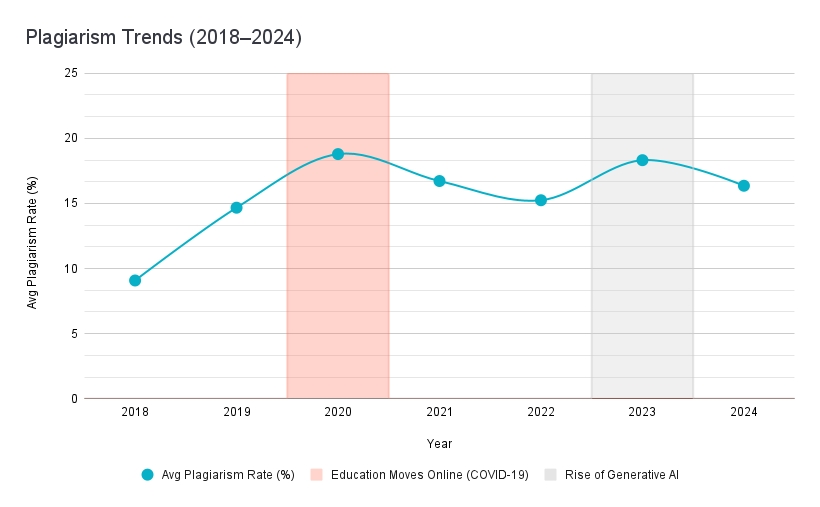
Figure 1. Global Average Plagiarism Rates (2018–2024), with COVID and AI periods highlighted.
Following this surge, 2021 and 2022 saw gradual declines in plagiarism rates, signaling an institutional adjustment to the remote learning environment. However, in 2023, a new spike emerged. The timing aligns with the global rise of generative AI tools, many of which became freely accessible and capable of producing high-quality written content. The average plagiarism rate rose by over 20%. In 2024, a notable drop of more than 10% occurred, which may indicate improved detection systems, clearer institutional policies, or increased awareness among students.
The report provides a country-level analysis across more than 90 nations. Case studies include Bangladesh, which experienced an early peak in 2019, followed by continuous improvement; Germany, which maintained some of the lowest rates throughout the period; and the United States, which saw one of the most dramatic spikes in 2020. These variations underscore how local context plays a critical role in shaping academic behavior.
This comprehensive dataset is now available in downloadable PDF reports. It serves as a valuable reference for researchers, policymakers, educators, and institutional leaders working to uphold academic standards in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
The full analysis and visualized trends can be accessed at: https://plagiarismsearch.com/global-plagiarism-trends
To access the full analysis:
Media Contact
Company Name: PlagiarismSearch.com
Contact Person: Marketing Lead
Email: Send Email
City: Alicante
Country: Spain
Website: https://plagiarismsearch.com




